Connect With Us
Osteomyelitis
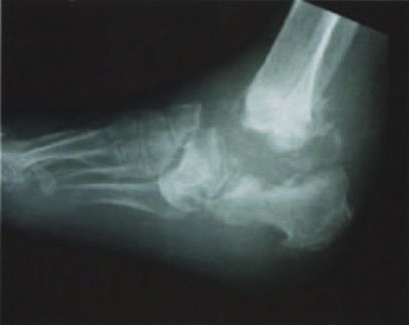 Osteomyelitis is a type of bacterial bone infection that moves from acute to chronic phases quickly. The infection usually begins in another part of the body and spreads to the bone via blood. Traumatic injury, frequent medication injections, the use of a prosthetic device, and some surgical procedures can increase susceptibility to the underlying infection.
Osteomyelitis is a type of bacterial bone infection that moves from acute to chronic phases quickly. The infection usually begins in another part of the body and spreads to the bone via blood. Traumatic injury, frequent medication injections, the use of a prosthetic device, and some surgical procedures can increase susceptibility to the underlying infection.
Diabetic patients who suffer from chronic wounds/ulcers are at higher risk for osteomyelitis, which almost always leads to partial amputations of the foot. Osteomyelitis infections are very difficult to cure with oral or intravenous(IV) antibiotics and surgical removal of the infected bone is usually requied.
The presence of bone infection can be diagnosed with tests, such as bone scans and MRI.
Osteomyelitis (an infection of the bone) can be caused by a variety of microbial agents (bacteria, fungus), the most common of which is staphylococcus aureus.
This serious infection can occur from a number of sources:
- It may enter bone through an injury, such as an open fracture with the bone ends piercing the skin.
- It can spread from elsewhere in the body or through the bloodstream.
- It can result from a chronic foot wound or infection, such as a diabetic ulcer.
To diagnose the condition, the foot and ankle surgeon will examine the area and may order blood tests and x-rays or other imaging studies. Treatment options include surgery and antibiotic therapy. For additional information, read Diabetic Complications and Amputation Prevention.
